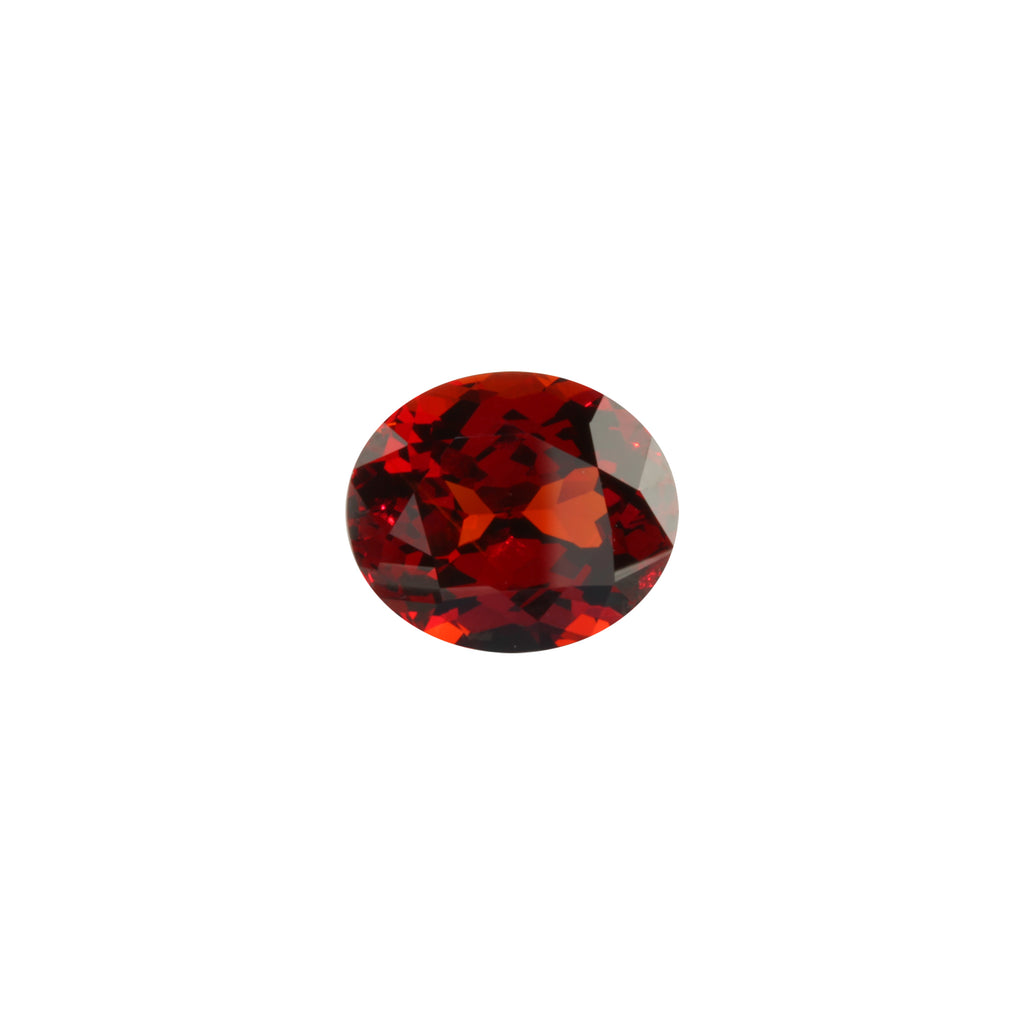
GARNET
Gemstone family: Garnet group
Crystal System: Cubic
Moh's scale of hardness: 6.5-7.5
Lustre: Vitreous to sub-adamantine
Birthstone: January
About: Garnet is a wide group of closely related mineral species with many varieties. Garnets range from red, brownish red, purplish red, orange, yellow to green. The most valuable varieties of garnets are tsavorites and demantoid garnets, both of which are green. Other desirable varieties of garnets are the purplish red Rhodolite and bright orange Spessartite and orangish-reddish-brown Hessonite. Some garnets display phenomena such as colour-change and asterism; the former refers to stones that change colour when seen under a daylight equivalent light source and under incandescent lighting and the latter phenomenon when cabochon-cut stones have a whitish star on top of the dome.
Origin: The main sources of garnets are: Brazil, Tanzania, Kenya, Madagascar, Russia, Sri Lanka, Brazil and India.
Use in jewellery: Garnets have a vitreous to sub-adamantine lustre; they rates 6.5-7.5 on the Mohs scale which makes them suitable for jewellery that has secure settings to protect the stones from wear. Depending on the transparency of the stone which can be anything between transparent to semi-translucent, garnets are cut into faceted gems, cabochons and beads.
Treatments, synthetics and imitations: Garnets are not usually treated and they have not yet been synthetically grown. Materials that are most commonly used to imitate garnets are: CZ , lab-made YAG (yitrium aluminium garnet), glass and plastic.